Drinking water and getting poisoned? Sodium and chlorine reported critical values.
Original Sun Jing Laboratory Medicine Network
Author: Sun Jing
Audit: Zhao Advanced
SETTING: People’s Hospital of Changzhi City, Shanxi Province
What is water poisoning? How can drinking too much water be toxic? Do many people think that drinking more water is good for health? Water is the source of life and an indispensable part of life. Especially in special circumstances such as physical discomfort or loss of appetite, doctors or family members even told us to drink more water. Isn’t that the more good substances, the better? We all know that any substance in the body is maintaining its relative balance, and water is no exception. It accounts for 65%-70% of the human body, and it can freely enter and exit the human cell membrane, maintaining the balance between water and electrolyte. Once this balance is broken, a series of symptoms will appear. [1]
Excessive drinking water, commonly known as "water poisoning", was reported in the United States, Canada, Germany and other countries as early as the 1930s. Today we will discuss the cases that happened around us.
First, the course of the case
On November 10th, 2020, as usual, we started a busy and regular testing work, and the critical value of an electrolyte caught my attention. The concentration of sodium ion (Na+) is 107.2 mmol/L, and the concentration of chloride ion (Cl-) is 73.7 mmol/L.. After re-checking, it is confirmed that it is correct, and immediately enters the process of processing and reporting the critical value. While calling the nurse to register the critical value, it contacts the competent doctor to ask about the patient’s situation.
The basic condition of the patient is a middle-aged woman, who has had irregular menstruation, increased leucorrhea, abdominal distension, occasional pain and loss of appetite in the past 2 months. Therefore, on the morning of November 10, the outpatient doctor asked for a B-ultrasound examination of the uterine appendix, and then drank a lot of water for B-ultrasound examination. No abnormalities were found in the appendix and no pelvic effusion was found. At this time, the patient suddenly became listless, general weakness, dizziness, visual rotation, mild headache, nausea, abdominal discomfort, unstable walking, and bed rest failed to alleviate. Immediately admitted to the gynecology department of our hospital.
After hospitalization, he suddenly lost consciousness, and his limbs twitched, and his symptoms were further strengthened. He urgently invited the Department of Psychiatry for consultation, and urgently checked a series of examinations such as electrolytes, blood routine, CT, skull MR and dynamic EEG. Physical examination at that time: temperature 37℃, pulse 63 times/minute, blood pressure 112mmHg/60mmHg. There was no abnormality in heart and lung auscultation, and no pathology was caused. At this time, the critical value of the laboratory returned to the doctor in charge, and the initial diagnosis of "hyponatremia and hypochloremia, water poisoning" was transferred to the neurology department of our hospital. After supplemented with concentrated sodium chloride and other treatments, there was no epileptic seizure. The skull MR showed that there was no obvious abnormality in the skull, no abnormality in dynamic EEG, and CT, blood routine and liver and kidney function were normal. The following are the changes of electrolyte sodium ion and chloride ion before and after treatment:
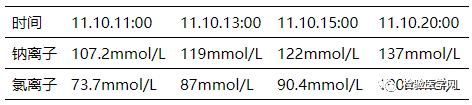
After treatment, all the indexes returned to normal, and he was discharged from the hospital on November 12, and there was no recurrence of the disease since he was discharged from the hospital by telephone.
Second, case discussion and analysis
Let’s analyze and summarize this case later. The first problem to understand is why there are mental symptoms of water poisoning. Excessive water refers to the fact that the total amount of water entering the body exceeds the displacement caused by various reasons, which leads to water retention in the body, often accompanied by electrolyte disorder, and the severe case is called water poisoning. It is generally considered that drinking more than 3 liters of water in a day is excessive intake, which is called polydipsia or polydipsia [2]. It is common in chronic mental patients, especially in schizophrenics. In addition, it will be caused by the obstacle of water regulation mechanism, without limiting drinking water or improper rehydration, or drinking a lot of water in a short time.
In addition, the bladder needs to be filled during gynecological examination, which is conducive to improving the accuracy of the examination. Drinking a lot of water in a short time, water is absorbed into the blood, which leads to the decrease of osmotic pressure in the blood, the decrease of reabsorption of water by distal renal tubules, the increase of urine volume and the increase of urine in the bladder. However, when the disease destroys the regulatory mechanism of the body or goes beyond the regulatory capacity, the balance of water, electrolyte and acid-base in the body will be broken, and water poisoning will occur in severe cases. Just like the above cases, patients with acute water poisoning have a very urgent onset. In just a few hours, neuropsychiatric symptoms are very prominent, mental disorders and epileptic seizures may cause very serious and dangerous consequences if they are not treated and diagnosed in time. [3.4]
Therefore, in our practical work, clinicians and B-ultrasound doctors must pay attention to whether there are clinical manifestations of water poisoning after drinking a lot of water when they need to hold their urine during B-ultrasound examination. In addition to the above reasons, there are primary and secondary causes of water poisoning, such as excessive secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), renal dysfunction, water and sodium metabolism disorder, insufficient drainage function of the body, hypotonic dehydration and so on. In addition, it should be noted that if the blood sodium rapidly drops below 108mmol/L within 48 hours, it will cause permanent damage to the nervous system or death [5], so we must pay enough attention to it in clinic to avoid irreversible adverse events.
Third, how to drink water scientifically
The concept of scientific health preservation and health care has entered every family. About how to drink water. How to drink water scientifically? Is the concern of most of us. The following suggestions can be shared with you:

1. Drinking water is not the only source of water intake: for ordinary people, the amount of water needed by the body to digest food and metabolize every day is about 2 liters [1]. Our intake depends on many factors, including health, activity intensity and living environment, and is also closely related to factors such as diet.
2. After exercise, you should pay attention to drinking water: don’t drink ice water, you can drink some salty water. [1]
3. Scientific drinking methods: drink slowly with a small mouth, drink boiled water or pure water, and drink less sugary drinks; Drink a small amount, drink more, and don’t drink too much; Drink less water just after eating [1].
[References]
1. Shen Zhengri. What is water poisoning? Health and wellness of traditional Chinese medicine, 2020,6(10).29-31.
2. Chen Hao, Liu Jinghui. Water poisoning caused by drinking a lot of water in schizophrenia. China Journal of Neurology, 2007,33 (7); 443-444
3. Xiang Hongbing. Acute water poisoning caused by drinking plenty of water before B-ultrasound examination. Modern Medicine, 2011, 39 (2); 189-190
4. Ye Rengao, Lu Zaiying. Internal Medicine [M] 6th Edition. Beijing People’s Medical Publishing House, 2004: 842-848.
5. Yu Dongshan, edited by Gao Zhenzhong. Handbook of Rational Drug Use in Psychiatry. Nanjing Jiangsu Science and Technology Press, 2005.92-95.
Original title: "Drinking water is actually poisoned? Sodium and chlorine reported critical values.
Read the original text