Frontier | Please check! The latest scientific research information of Dongda!
Spring is getting stronger in the middle of March.
The scientific research work of Dongda University is also in full swing.
Let’s follow the official micro-view.
Recent scientific research in Dongda University!

Highlights and tours
01
Scientific and technological trends
Trends in Science & Technology
01 Southeast University held the deployment meeting of scientific research in 2023.
The team of Professor Xiao Rui and Professor Zhang Huiyan made important progress in the field of high-value utilization of biomass.
Professor Yang Hong’s research group developed a high-performance soft-jumping robot imitating collembola.
Team Zhang Yuanjian made significant progress in the evaluation of fuel cell catalysts.
Li Quan’s team made important research progress in light-driven molecular motors.
Zhao Chunjie’s team has made important progress in the development of cerebral cortex and posterior cortex.
07 POCT research group Hao Qing and researcher Liu Hong published the latest research results in NatureCommunications.
Two papers directed by Professor Wang Xiaoyang for doctoral students were published in the internationally renowned journal Religions(A&HCI).
09 Professor wujun’s research group published the latest research results of full-attribute gel electronic skin in ACS Nano.
News and details
one
Southeast University held the deployment meeting of scientific research in 2023.

In order to strengthen "organized scientific research" and comprehensively and effectively promote the scientific research work of the school, on the afternoon of March 10th, the deployment meeting of scientific research work of Southeast University in 2023 was held in Jiulonghu Campus. WU GANG, Executive Vice President, responsible comrades of the Academy of Research, and research deans of various institutes attended the meeting.
After listening carefully to the report, WU GANG first affirmed the achievements made by various colleges in scientific research organization in 2022, and put forward three requirements at the same time: First, he asked the scientific research deans of various colleges to enhance their sense of initiative, implement "organized scientific research", encourage researchers to explore freely in the organized scientific research system, jump out of the limitations of scientific research indicators, and continuously deepen the optimization and reform of scientific research system and mechanism; Second, colleges are required to do an organized "external circulation", and take the institutional platforms such as off-site research institutes and school-enterprise joint research and development centers as the starting point, vigorously strive for external resources and development opportunities, and break through the resource bottleneck encountered by colleges in the development process; The third is to ask the research deans of various colleges to take the initiative, make scientific research management practical and detailed, mobilize and plan as soon as possible, and do targeted services well. Finally, WU GANG emphasized that all colleges should promptly and effectively publicize the ideas and key work arrangements of the school’s scientific research work to researchers, ensure the efficient development of scientific research throughout the year, and constantly promote the innovative and high-quality development of the school’s scientific research.
2
The team of Professor Xiao Rui and Professor Zhang Huiyan is at
Important progress has been made in the field of high-value utilization of biomass
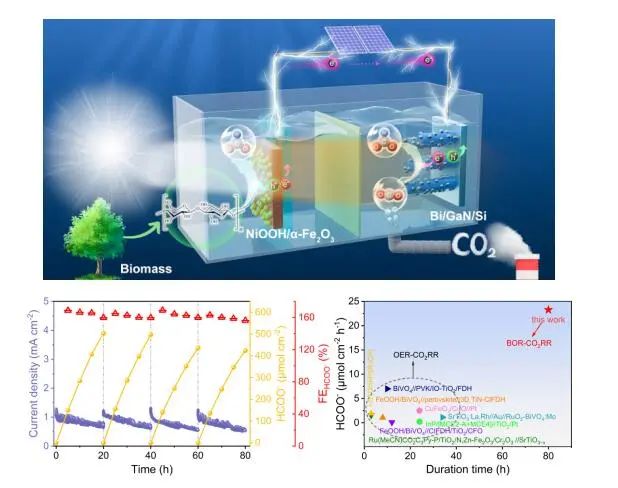
Recently, the clean energy team led by Professor Xiao Rui and Professor Zhang Huiyan from the School of Energy and Environment of Southeast University published a paper entitled "Renewable form from sunlight, biomass and carbon dioxide in a photoelectrochemical cell" in the internationally renowned journal Nature Communications, and reported the latest research results of the team in renewable synthetic fuels and high-value utilization of biomass.
In this work, the team developed and designed a photoelectrocatalytic system with high selectivity to break the C-C bond of biomass. With glucose as a mold, the selectivity of C-C bond breaking to formic acid on the photoanode is close to 100%. Using poplar sawdust, rice straw or bamboo as raw materials, the selectivity of formic acid is over 90%. The reaction is a continuous C1-C2 bond-breaking process, through which aldose with smaller molecular weight is continuously generated, and finally becomes formic acid. In addition, the coupling and matching of photoanode biomass oxidation and photocathode CO2 reduction can realize the co-catalysis of anode and cathode to produce formic acid without bias driven by sunlight, and the comprehensive Faraday efficiency of the system exceeds 160%, which breaks through the limit of the traditional photoelectric catalysis system without biomass. This work provides a new way for the high-value utilization of biomass resources.
three
Research Group of Professor Yang Hong from Southeast University
Research and development of high-performance soft jumping robot imitating bullet tail worm
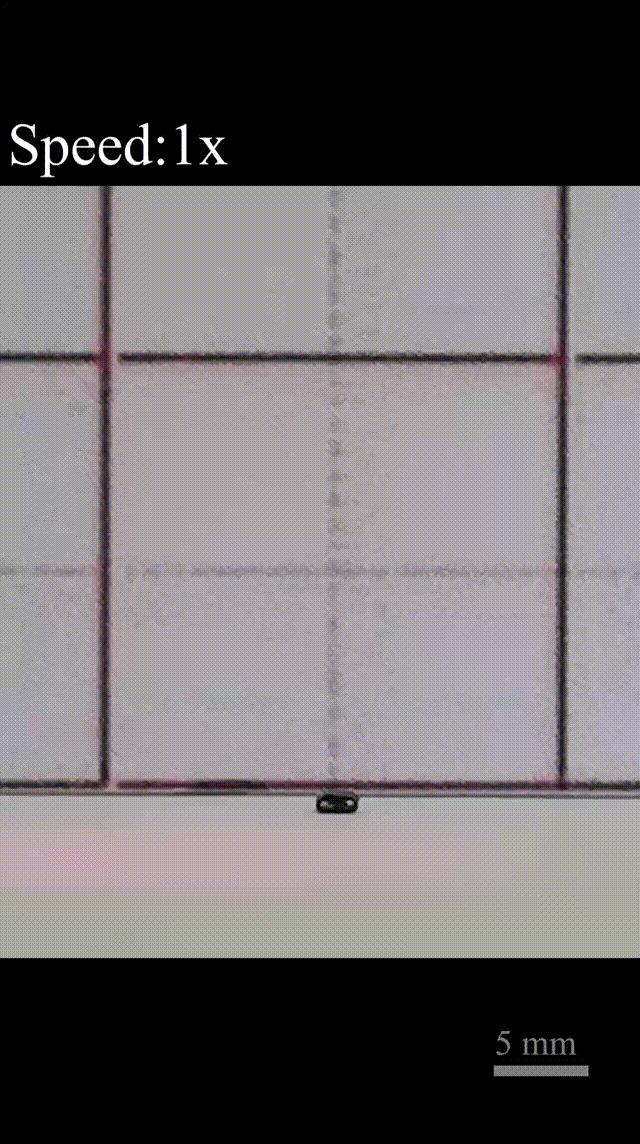
Recently, the research group of Professor Yang Hong from Institute of Intelligent Materials and School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Southeast University has made important progress in the research field of optically controlled soft drives, and developed a soft robot with excellent jumping performance. The research results were published in the top international journal Angew. Chem. int.ed. and were selected as VIP papers.
Inspired by the jumping mode of Springtail, Professor Yang Hong’s research group designed a liquid crystal elastomer-based soft jumping robot with Three-leaf panel fold structure based on the slingshot ejection principle. Compared with the jumping robot driven by heat, light, gas, electricity, magnetism and solvent developed by predecessors, the soft robot has better jumping ability, with its maximum jumping height and jumping distance reaching 87 times and 65 times of its own length respectively (equivalent to an adult jumping to the height of 50 stories), and it can realize continuous jumping under different environmental conditions.

four
Team Zhang Yuanjian of Southeast University is at
Important progress has been made in the evaluation of fuel cell catalysts.
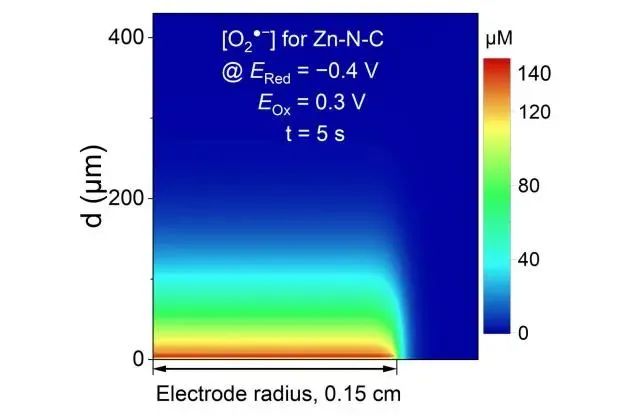
Recently, the research group of Professor Zhang Yuanjian from the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Southeast University and the Engineering Laboratory of Carbon-rich Materials and Devices in Jiangsu Province reported a new method for rapidly, accurately and comprehensively evaluating fuel cell electrocatalysts. The related achievements were published online in the international authoritative academic journal angew.chem.int.ed. in the form of Hot Paper with the title of "Elucidating Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction via intermediaries by time-dependent electrochemistry".
Professor Zhang Yuanjian’s research group proposed to establish the reaction rate equation through the formation of reactive oxygen intermediates, and used ultra-sensitive time-dependent electrochemiluminescence detection technology to evaluate the kinetics of electrocatalytic oxygen reduction in alkaline medium. It was found that the performance of electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction could be quickly classified by electrochemical luminescence intensity. More importantly, because of the ultra-sensitive quantitative chemical reaction between the active oxygen intermediate and the electrochemiluminescence reagent, not only the apparent rate constant of oxygen reduction was obtained by analyzing the decay curve of electrochemiluminescence, but also the kinetic information of the time and space distribution of the active oxygen intermediate at different potentials was successfully obtained for the first time.
five
Li Quan’s team is working on light-driven molecular motors
Make important research progress

Recently, Li Quan, Dean of the Institute of Intelligent Materials of Southeast University and College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, has made important progress in the chiral inversion and reversible adjustment of circularly polarized light driven by visible light. The related research results are as follows: "Reversible handiness investment and circular polarized light reflection tuning in self-organized mechanical superstructure using visible-light- The title "Driven Macro Cyclic Chiral Switches" was published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition, which was selected as the Hot Paper and the cover of the current issue. Li Quan is the only correspondent of the paper.
Chiral adjustment and chiral inversion of new topological molecular materials have always been the focus of scientific research. Chirality adjustment with photomolecular motor can bring convenient adjustment methods. However, the traditional photomolecular motor needs high-energy ultraviolet light to drive, so it is an ideal solution to develop an environmentally friendly molecular motor with visible light regulation. Based on this, Li Quan’s team reported that a series of ring-shaped photomolecular motors can be driven by visible light to chirally regulate the induced spiral liquid crystal superstructure. This kind of ring-shaped molecular motor is of great significance to the development of multifunctional light-driven molecular framework and its application in molecular machines, and also provides a research and development basis for a wider range of environmentally friendly intelligent materials.
six
Team Zhao Chunjie is at
The field of development of cerebral cortex and posterior cortex.
Make important progress
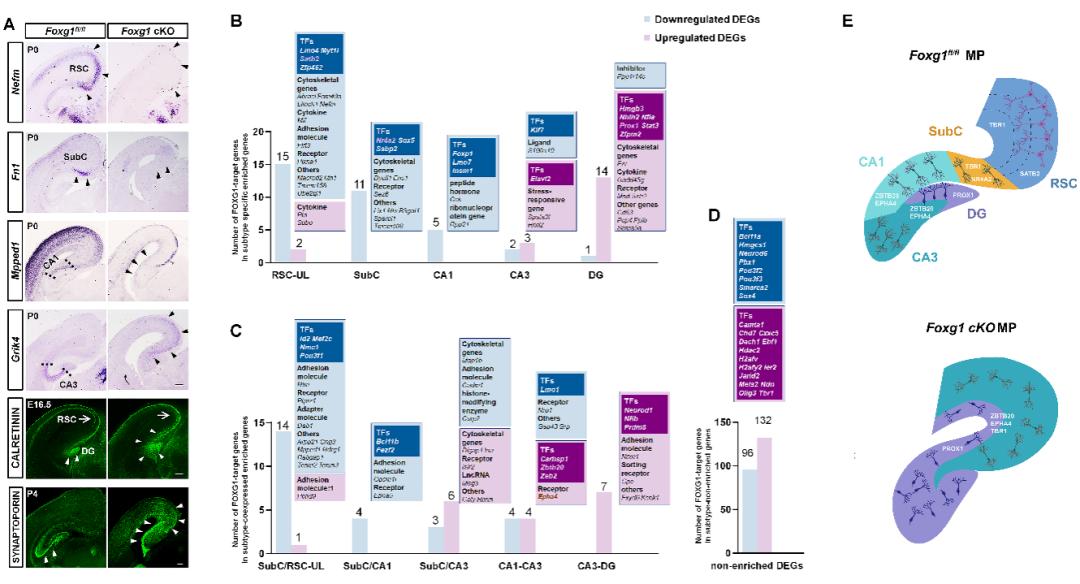
Recently, Southeast University School of Medicine, The research team of Zhao Chunjie, the Key Laboratory of "Genes Related to Development and Disease" of the Ministry of Education, published a publication entitled Fox G1 Drives Transcript Omic Networks to Specify Principal Neurosubtypes During the Development of the Science Advances. Medial pallium’s research paper (Baru, Ph.D. student of Southeast University, and Yang Lin, Ph.D. student of Fudan University, are the first co-authors).
This study focuses on the risk gene FOXG1 of FOXG1 syndrome. Previous studies have shown that the mutation of FOXG1 gene can trigger FOXG1 syndrome, and patients show microcephaly, developmental retardation, mental retardation, social withdrawal behavior, stereotyped movement language disorder and epilepsy. By establishing conditional Foxg1 knockout mice, combining with single cell sequencing, ChIP-qPCR and intrauterine embryo electrotransformation, this study analyzed the specialized mechanism of FOXG1 regulating different types of excitatory projection neurons in CA1-CA3, dentate gyrus, hypothalamus and retrocompression cortex, and revealed the regulation of gene transcription in the development of paleocortex and retrocompression cortex. It is helpful to understand the biological basis of advanced brain functions such as learning and memory, spatial orientation and emotional regulation, deepen people’s understanding of the pathogenesis of diseases such as FOXG1 syndrome and autism spectrum disorder, and provide new clues for developing early diagnosis methods of related neuropsychiatric diseases and finding intervention targets.
seven
POCT research group Hao Qing, researcher Liu Hong, etc.
In "NatureCommunications"
Publish the latest research results
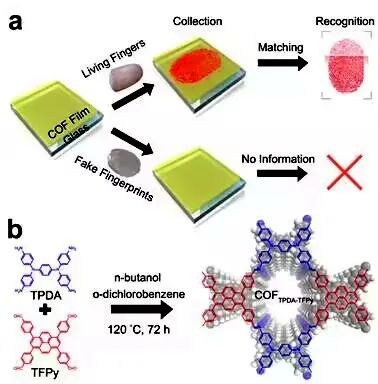
Recently, Hao Qing, POCT research group of bioelectronics State Key Laboratory of Southeast University and School of Biological Sciences and Medical Engineering, Researcher Liu Hong cooperated with researcher Dong Wang from Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences to publish the latest research results titled A Sweat-Responsive Covalent Organic Framework Film for Material-Based Livelihood Detection and Sweat Pore Analysis online in the internationally renowned academic journal Nature Communications. This study reports a covalent organic framework (COFs) material with stable color-changing response to human sweat. This smart thin film material can collect fingerprints and sweat pore distribution images, and can be applied to fingerprint in vivo detection and skin disease analysis (Nature Communications 2023, DOI: 10.1038/S41467-023-36291-9).
In this work, an intelligent COF material with sweat response function was designed. When exposed to human sweat, COFTPDA-TFPy film will change from light yellow to deep red. When the COFTPDA-TFPy film is touched by a human finger, it can produce a fingerprint pattern visible to the naked eye through the color change caused by sweat secretion from the hand. When this COF is used as a fingerprint collection material, the real fingerprint can be easily collected, but the artificial silicone fake fingerprint can’t leave any information, so the real finger can be visually distinguished from the fake fingerprint with 100% accuracy. This strategy is defined as "material-based in vivo detection strategy". Previously, fingerprint in vivo detection was realized by computer image processing. This work proposed a new in vivo detection strategy from the perspective of material science, and achieved a 100% success rate.
eight
Professor Wang Xiaoyang directs doctoral students.
Two papers in internationally renowned journals
Published by Religions(A&HCI)
Recently, as a correspondent, Wang Xiaoyang, the chief expert of think tank of Southeast University and a professor of art college, has published papers in internationally renowned journals Religions(A&HCI, CITESCORE 1.0) in collaboration with doctoral students Han Jing and Shi Yizhen.
The thesis with Han Jing is: A Comparative Study of Religions Images on Sogdian Burial Utensils in China and Central Asia. The study of Sogdian is an outstanding academic field in the world, and China scholars rarely participate in the study of Sogdian outside China. This paper relies on the major national social science project "History of Religion and Art in China" (No.:17ZDA237) which has been completed by Professor Wang Xiaoyang, and extends to overseas archaeology in the Central Asian section of the Belt and Road. For the first time, the number and types of Sogdian funerary wares in China and Central Asia are statistically analyzed, and six targeted tables are made. The judging experts believe that this paper has detailed data, which is of great significance to the understanding of China Sogdian studies in the West, and it is also a rare comparative research achievement of China scholars at present.
The thesis with Shi Yizhen is: A Spatial Study of the Relics of Chinese Tomb Murals. Space research is a newly emerging research field in recent years. This paper is based on the national social science key project "Study on the Archaeological Chronicle of Religious Art in China" (No.:17AZJ002) which has been completed by Professor Wang Xiaoyang. It is the first attempt to use GIS tools to visualize the remains of tomb murals, design a three-level index system to cover the information of more than 1,000 tomb murals, and make 24 visual images.

nine
Professor wujun’s research group is in ACS Nano.
Publish the latest research results of full-attribute gel electronic skin
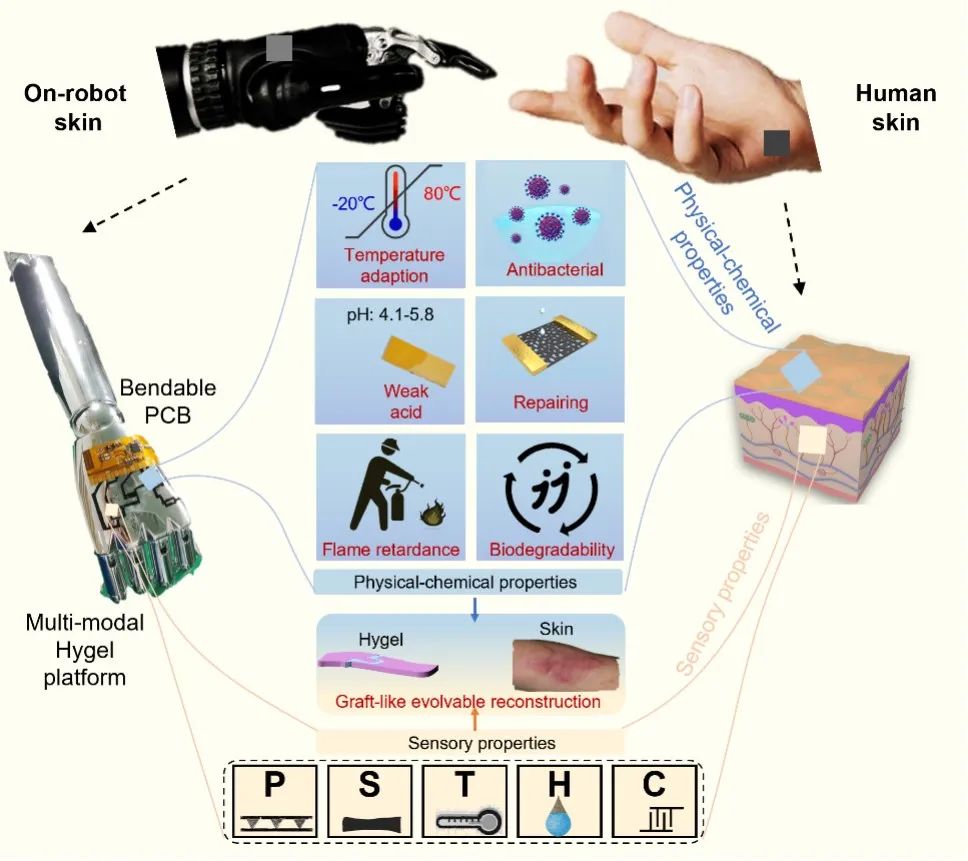
Recently, the research group of Professor wujun from the School of Electronic Science and Engineering of Southeast University published the latest research results titled "Water-Modulated Biometric Hyper-Attribute-Gel Electronic Skin for Robotics and Skin-Attachable Wearable" online in the internationally renowned academic journal ACS Nano.
Tactile sensor is listed as one of the key "stuck-neck" technologies alongside mask aligner and chip by Chinese Academy of Sciences. In recent years, the research group has devoted itself to researching the bionic multi-mode soft tactile sensor by means of natural interface structure bionic and material modified skin function bionic, further developing the man-machine intelligent interface system driven by the bionic multi-mode soft tactile sensor, and promoting its forward-looking application in major national strategies such as eye health, ergonomics and interaction, machine tactile, etc. Related achievements have been published in famous journals such as ACS Nano, Research, Nano Energy, Nano Research, Advanced Intelligent Systems, etc.
At present, the mainstream work of electronic skin includes: ① improving the perception properties of single or several stimuli (pressure, temperature, etc.); ② Study the combination of some physical and chemical properties and perceptual properties. Usually, this kind of work only covers two or three attributes of the skin, which is far from realizing the sensory and physical and chemical characteristics of skin-like stimulation perception. Covering all the physical-chemical and sensory characteristics of human skin is the next milestone to realize more complex multifunctional bionic applications and the next generation of artificial skin.
Be famous for science and serve the country with talents.
Dongda people are always on the road!
Like the researchers at Dongda University ~
Xin media studio
Original title: "Frontier | Please check! The latest scientific research information of Dongda! 》
Read the original text